Access Virtual Machines' graphic console using noVNC
Introduction
NoVNC is a JavaScript VNC client using WebSockets and HTML5 Canvas. We provide websocket api for VNC access under
APISERVER:/apis/subresources.kubevirt.io/v1alpha3/namespaces/NAMESPACE/virtualmachineinstances/VM/vnc
but we can not access the VNC api directly since authorization is needed. In order to solve the problem, we provide a component using kubectl proxy to provide a authorized vnc acess, we name this Component virtVNC.
In this post we are going to show how to do this in detail.
The detailed method
Prepare Docker Image
First prepare docker build dicrectory.
mkdir -p virtvnc/static
Then clone noVNC files from github.
git clone https://github.com/novnc/noVNC
And then copy noVNC files to docker build directory.
cp noVNC/app virtvnc/static/
cp noVNC/core virtvnc/static/
cp noVNC/vender virtvnc/static/
cp noVNC/*.html virtvnc/static/
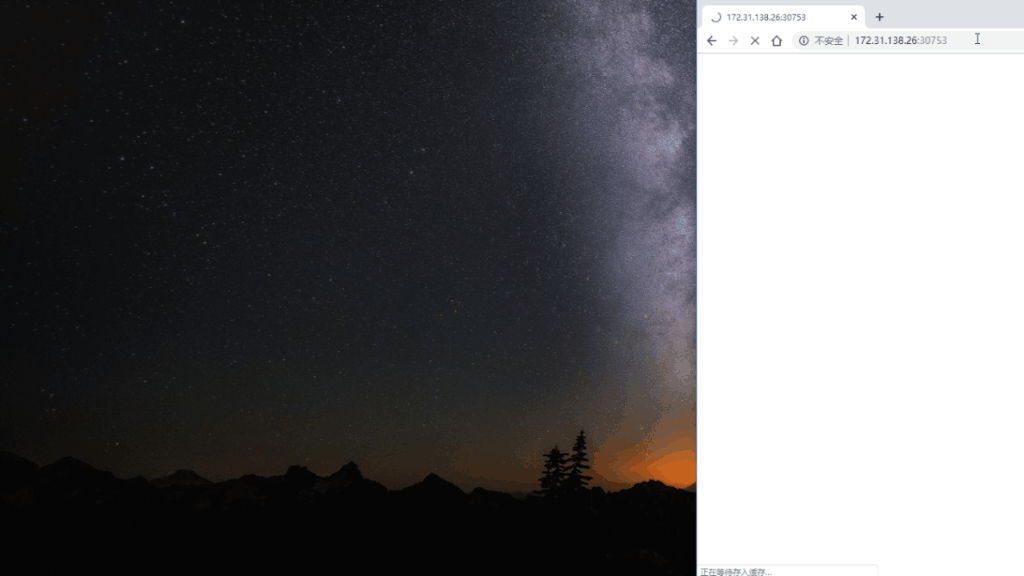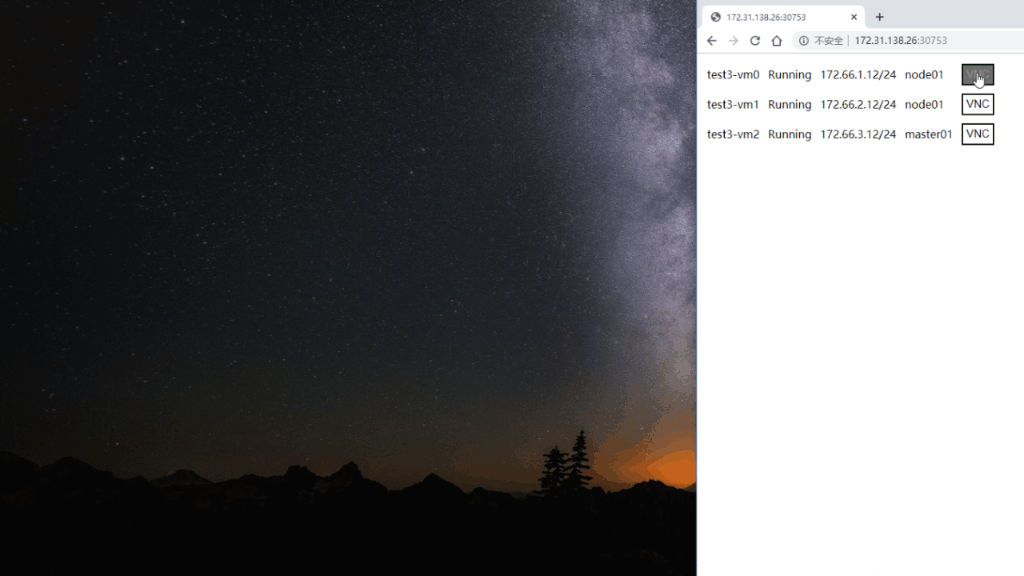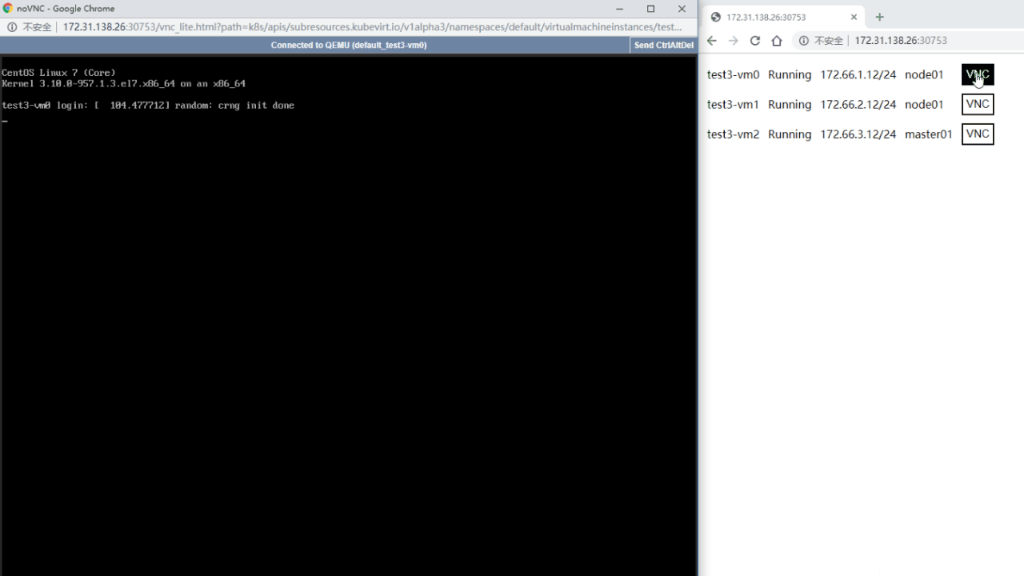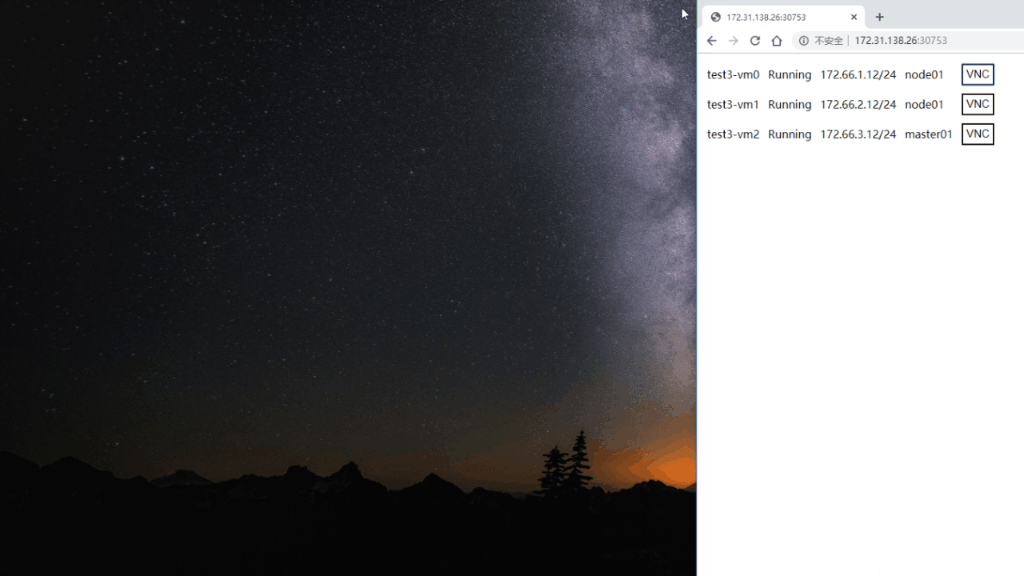
Create a file index.html to virtvnc/static/ with the following content. The page will display VMs and corresponding VNC links.
<html>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
td {
padding: 5px;
}
.button {
background-color: white;
border: 2px solid black;
color: black;
padding: 5px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
-webkit-transition-duration: 0.4s;
transition-duration: 0.4s;
}
.button:hover{
background-color: black;
color: white;
cursor: pointer;
}
button[disabled] {
opacity: .65;
}
button[disabled]:hover {
color: black;
background: white;
}
</style>
<!-- Promise polyfill for IE11 -->
<script src="vendor/promise.js"></script>
<!-- ES2015/ES6 modules polyfill -->
<script nomodule src="vendor/browser-es-module-loader/dist/browser-es-module-loader.js"></script>
<script type="module" crossorigin="anonymous">
import * as WebUtil from "./app/webutil.js";
const apiPrefix='k8s/apis'
function loadVMI(namespace) {
WebUtil.fetchJSON('/' + apiPrefix + '/kubevirt.io/v1alpha3/namespaces/' + namespace + '/virtualmachineinstances/')
.then((resp) => {
let vmis = [];
resp.items.forEach(i => {
let tr = document.createElement('tr');
tr.innerHTML="<td>" + i.metadata.name + "</td><td>" + String(i.status.phase) + "</td><td>" + String(i.status.interfaces !== undefined ? i.status.interfaces[0].ipAddress : '') + "</td><td>" + String(i.status.nodeName !== undefined ? i.status.nodeName : '') + "</td><td><button class='button' " + String(i.status.phase =="Running" ? "" : "disabled") + " onclick=\"window.open('vnc_lite.html?path=" + apiPrefix + "/subresources.kubevirt.io/v1alpha3/namespaces/" + namespace + "/virtualmachineinstances/" + i.metadata.name + "/vnc', 'novnc_window', 'resizable=yes,toolbar=no,location=no,status=no,scrollbars=no,menubar=no,width=1030,height=800')\">VNC</button></td>";
document.getElementById("vmis").appendChild(tr);
});
if (resp.items.length === 0) {
document.body.append("No virtual machines in the namespace.");
}
})
.catch(err => console.log("Failed to get vmis: " + err));
}
let namespace = WebUtil.getQueryVar('namespace', 'default');
loadVMI(namespace);
</script>
</meta>
<body>
<table><tbody id="vmis">
</tbody></table>
</body>
</html>
Create dockerfile with following content to add static html files and set up kubectl proxy command line args.
FROM quay.io/bitnami/kubectl:1.15
ADD static /static
CMD ["proxy", "--www=/static", "--accept-hosts=^.*$", "--address=[::]", "--api-prefix=/k8s/", "--www-prefix="]
Finally use docker build to build docker image.
cd virtvnc
docker build -t quay.io/samblade/virtvnc:v0.1 .
Setting Up RBAC
Create a service account for virtvnc.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: virtvnc
namespace: kubevirt
Then define cluster role for kubevirt, setting up permissions needed.
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: virtvnc
rules:
- apiGroups:
- subresources.kubevirt.io
resources:
- virtualmachineinstances/console
- virtualmachineinstances/vnc
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- kubevirt.io
resources:
- virtualmachines
- virtualmachineinstances
- virtualmachineinstancepresets
- virtualmachineinstancereplicasets
- virtualmachineinstancemigrations
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
And then binding cluster role to service accout.
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: virtvnc
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: virtvnc
namespace: kubevirt
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: virtvnc
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Deploy to kubernetes
Create following yaml, and then apply to kubernetes to setup virtvnc deployment.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: virtvnc
namespace: kubevirt
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: virtvnc
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: virtvnc
spec:
serviceAccountName: virtvnc
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/master: ""
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Equal"
value: ""
effect: "NoSchedule"
containers:
- name: virtvnc
image: quay.io/samblade/virtvnc:v0.1
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
port: 8001
path: /
scheme: HTTP
failureThreshold: 30
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
successThreshold: 1
timeoutSeconds: 5
Expose a NodePort service, then we can access the web page from node network.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: virtvnc
name: virtvnc
namespace: kubevirt
spec:
ports:
- port: 8001
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8001
selector:
app: virtvnc
type: NodePort
Note
This will make all your virtual machines vnc & console accessible to node network.**
The Simple Way
In this github repo and registry you’ll find a ready to use version of the above which you can deploy in a single command like this:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/wavezhang/virtVNC/raw/master/k8s/virtvnc.yaml
Access VNC
First get node port of virtvnc service.
kubectl get svc -n kubevirt virtvnc
Then visit the following url in browser:
http://NODEIP:NODEPORT/
If you want manage virtual machines in other namespace, you can specify namespace using query param namespace like following:
http://NODEIP:NODEPORT/?namespace=test